
In hazardous areas with explosive dust, gases, and vapors, such as coal powder, flour, aluminum powder, hydrogen gas, etc., static electricity may cause fires or explosions, posing a great danger. Therefore, in explosive hazardous areas, the use of insulation materials should be minimized as much as possible. When selecting electrical insulation materials, it is advisable to consider maintainingZhongnuo TestingMinimum insulation resistance to prevent discharge when exposed non-metallic components come into contact with live parts. For non-metallic insulation materials, the anti-static ability of the equipment can be evaluated by measuring the surface resistance of the equipment casing.
Surface resistance, measured in ohms, refers to the resistance between two electrodes in contact with the measured surface.
According to the requirements of the IEC60079 series of standards:
At a relative humidity of ≤ 100 G Ω and (30 ± 5)%.
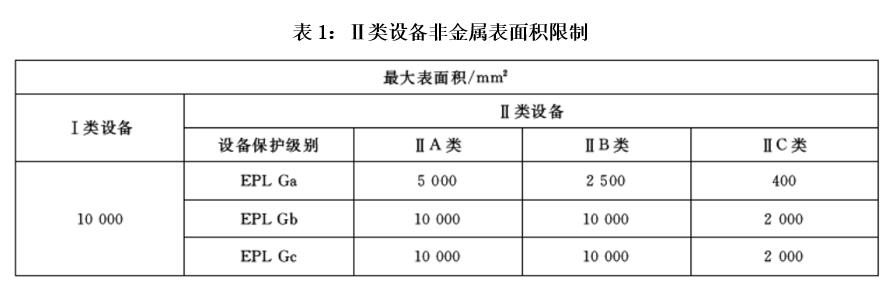
2. In Class III explosive dust environments, if the surface area of the non-metallic casing of electrical equipment does not exceed 500mm2, the risk of static electricity may not be considered; If the limit is exceeded, surface resistance testing verification is required. The determination requirements are the same as the limit values for surface resistance testing in Class II gas environments mentioned above. For fixed installation equipment that cannot meet the surface resistance limit, it can be usedstayexplosion-proofsignAdd "X" after the device, and inform the user in the user manual by adding corresponding warning signs.
Original article, plagiarism and reprinting are strictly prohibited!