
As a safety technology that suppresses the energy of ignition sources, intrinsic safety and explosion-proof certification technology has been widely used in engineering projects in various industries due to its advantages of simple structure, small volume, light weight, and the ability to maintain, calibrate, and replace parts with electricity.
Basic requirements for circuit design of intrinsic safety and explosion-proof
By controlling the electrical parameters of the circuit (such as reducing the parameters of energy storage components such as inductance and capacitance), or reducing the circuit current and voltage, the circuit can meet the requirements of intrinsic safety and explosion-proof; The components in the circuit should have sufficient power, and the connecting wires should have sufficient cross-section to ensure that the high voltage and large current that the circuit may generate under various fault conditions will not damage the performance of the components. The reliability of the components is ensured to ensure the reliability of the circuit. This requires the calculation of the corresponding electrical component parameters in the intrinsic safety circuit, i.e. intrinsic safety circuit calculation, to meet the requirements of relevant safety regulations and ensure safety production. When working normally, the safety factor is 2.0; When a fault occurs, the safety factor is 1.5; When there are two faults, the safety factor is 1.0.
The basic principle of intrinsic safety explosion-proof certification technology is to achieve the purpose of explosion-proof by limiting energy. Under normal or abnormal circuit conditions, intrinsic safety technology reliably limits the energy in the circuit within an allowable range to ensure that in the event of electrical equipment short circuits, component damage, etc., it does not cause the explosion of hazardous gases that may exist around it.
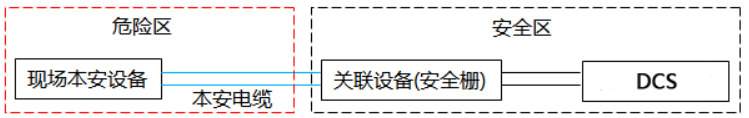
The intrinsic safety explosion-proof system, abbreviated as the intrinsic safety circuit system, consists of three parts: on-site intrinsic safety equipment, intrinsic safety cables, and associated equipment, as shown in Figure 1. The system circuit is divided into intrinsically safe circuits and non intrinsically safe circuits based on safety barriers. The circuit formed by connecting the safety barrier to the on-site instrument through an intrinsic safety cable is an intrinsic safety circuit; The circuit from the safety barrier to the DCS and to the power supply is a non intrinsically safe circuit.
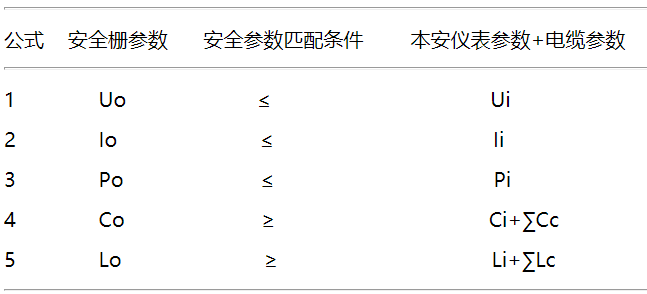
Several inequalities for calculating simple intrinsic safety circuits:
The copyright of this article belongs to Zhongnuo Testing. The right to pursue plagiarism and theft will be reserved. Reproduction must indicate the source of the original text.